What Recent Excavated Temple Remnants of Ram Janambhoomi Affirm

Ayodhya! This was the capital of the Kosala kingdom since Treta Yuga where the Ikshvaku dynasty flourished. This was the place where Shri Ram was born. According to historical records, Brihadbala was the last king of this dynasty, born 32 generations after Shri Ram. The region was under the influence of Raja Vikramaditya for some time under whose patronage several temples were built.
Shri Ram Janmbhoomi Teerth Kshetra, a Trust constituted to look after construction and management of Shri Ram Janambhoomi temple in Ayodhya, posted on May 20 images of temple remnants discovered from excavations at the site. The news created a stir across the country.
According to a tweet by the official twitter handle of the Trust, “The work started on May 11, 2020. Since then many objects have been discovered during excavation. It includes many objects of archaeological importance like flowers made of stone, Kalash, Aamalak, Dorjamb, etc.”
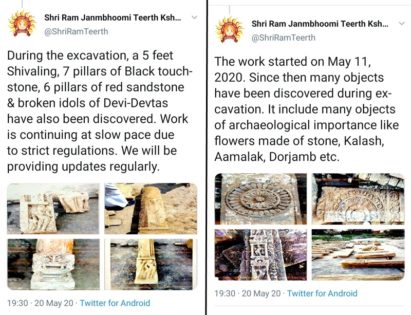
In another post, the handle tweeted with photographs: “During the excavation, a 5 feet Shivaling, 7 pillars of Black touchstone, 6 pillars of red sandstone & broken idols of Devi-Devtas have also been discovered. Work is continuing at slow pace due to strict regulations. We will be providing updates regularly.”
Vinod Bansal, National Spokesperson of Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP) released a press note, that reads thus:

It was on March 25 that Yogi Adityanath, the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh performed special puja and shifted Ram Lalla from the makeshift temple in Ayodhya to another pre-fabricated temple in the same premise. Due to the corona pandemic, public participation in the rituals was prohibited.
The discovered remnants of temple further justify the Ayodhya verdict. It all started on January 29, 1885 with the first lawsuit being filed by Raghubar Das, the Mahant of Ram Janambhoomi against the Secretary of State for India in Council to build a temple at the Ram Chabutara spot. And then the series of ‘tarikh par tarikh‘ by the Supreme Court!

Temple remnants recently discovered at Ram Janambhoomi site. Images source: Shri Ram Janmbhoomi Teerth Kshetra
It was in 1853 that two groups of Hindus and Muslims clashed over the Ram Janambhoomi site of worship in Ayodhya. A series of lawsuits were filed, the first by Raghubar Das as aforementioned. After independence of India, the first lawsuit was filed after 1949. Nirmohi Akhara, in the year 1959, claimed the disputed site by filing a lawsuit.
In 1961, the Uttar Pradesh Waqf Board also filed a case in court seeking possession of Babri Masjid. It was on September 30, 2010 that the Allahabad Court distributed the disputed land into three parts, giving each to Ramlalla Virajman, Nirmohi Akhara sect, and the Sunni Central Wakf Board, UP. But on May 9, 2011, this order was challenged before the Supreme Court and the verdict was stayed.

Temple remnants recently discovered at Ram Janambhoomi site. Images source: Shri Ram Janmbhoomi Teerth Kshetra
After a 40-day hearing, on November 9, 2019, the Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court of India awarded the entire disputed area in Ayodhya to the Hindus. The verdict included offering of an alternative land of 5 acres in Ayodhya to the Sunni Central Waqf Board for the construction of a mosque. During the hearing, CJI Ranjan Gogoi had referred to an Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) report and various other evidences. Padmashree Meenakshi Jain’s books Rama and Ayodhya and The Battle for Rama on the Ram Temple of Ayodhya further strengthened the case.

Lotus Chakra. Image source: Shri Ram Janmbhoomi Teerth Kshetra
There were different interpretations by experts on the temple remnants recently discovered. Vedveer Arya, who has expertise in reading inscriptions, epigraphs and carvings, said on the lotus chakra motif found in excavations at Ayodhya Ram Janmabhoomi, as a fascinating use of prime numbers by ancient Indians.
He further said, “Outer whorl has 29 equal petals and inner has 13 and center has 7. The formula is 7-13-29. These three are ‘prime’ numbers and the 360°circle not divisible by 7, 13 or 29. Our ancient Sulbasutras clearly demonstrate that using Shulba i.e. rope, a circle can be divided into any number of parts. Probably, 7 indicate 7 days of week, 13 petals indicate 13 lunar months (including one intercalary month) and 29 petals indicate 29 days of a lunar month.” Vedveer Arya is the author of Chronology of India.

Shivalinga recently discovered at Ram Janambhoomi site. Images source: Shri Ram Janmbhoomi Teerth Kshetra
The Shivalinga excavated from the Ram Janambhoomi site is typical of Shivalingas found across the country. During my research visits to temple ruins across the country, I came across similar Shivalingas adorning two external corners of a temple or all corners. Sometimes one Shivalinga adorns one corner. Similar Shivalingas also adorn garbhagrihas. Here is a similar Shivalinga I came across in a 10th century Shiva temple in ruins in the Sariska Tiger Reserve in Alwar, Rajasthan:

Shivalinga in a 10th century Shiva temple in ruins in Sariska Tiger Reserve in Alwar, Rajasthan. Photography by Manoshi Sinha.
The temple remnants like pillars, broken Moortis/carvings of deities, flowers made of stone, kalash, aamalak, doorjamb, etc. discovered at the Ram Janambhoomi site are typical of remnants discovered in 8th to 12th century temple group ruins in many parts of India, especially in the northern region. Most of these are also typical in many standing ruins of temples that have been restored and also in temples where worshipping has been continuing since centuries. This also suggests the Ram Janambhoomi temple site was a huge complex housing several temples dedicated to numerous deities once upon a time. We come across many groups of temple in India where there are Vaishnavism, Shaivism, and Shaktism shrines in one huge premise.
Meanwhile, a section of people, without even getting into the deep details of the findings in Ayodhya started tweeting under the hashtag BuddhismVsBrahmanism. A fake narrative has been doing the rounds on social media since long targeting divisions within two cultural identities of India. On the same ground, BuddhismVsBrahmanism was trending on twitter in India with 176k tweets after the findings in the Ram Janambhoomi site. While destruction of Buddhist heritage sites is mainly attributed to Islamic invaders who vandalized Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain sites, the fake narrative being spread since long in media and literature added fuel to the fire after the recent excavations in the place of birth of Shri Ram.
Buddha is considered as a Dashavatar, as one of the incarnations of Bhagwan Vishnu. Besides literary corroborations, there are many temple carvings dating back to the medieval period that justify the same. For example, the 8th-9th century Torana (arched gateway) of Vishnu (Dashavatar) temple at Gyaraspur in Madhya Pradesh has carvings of all the 10 Dashavatars.

Moortis of Buddha and Kalki in a panel in the Torana (arched gateway) of Vishnu (Dashavatar) temple at Gyaraspur, MP. Photography by Manoshi Sinha.
Here, Moortis of Buddha and Kalki are featured in one panel. Buddha here is depicted as an incarnation of Vishnu. This temple group (foundation bases of more temples other than the main shrine is visible) is spread across a huge area. Only the Torana and a Mandapa stand amid the ruins.
In this context, on the BuddhismVsBrahmanism hashtag, Maria Wirth, author of Thank You India tweeted, “Attacks on Hindus from all sides…. Now #BuddhismVsBrahmanism is made to trend, obviously instigated. It’s nasty. They may be frightened that Hindu unity spoils their agenda of wiping out Hindu/Sanatana Dharma, therefore all out attack.”

Recently The Caravan magazine published a fake narrative quoting DN Jha turning victims to perpetrators and vice versa. Trying to prove Muslim historians of even Khilji’s period wrong! Persian historian Minhaj-i-Siraj in his book Tabaqat-i Nasiri wrote about how Bakhtiyar Khilji destroyed Nalanda University. He was the principal historian of the Mamluk Sultanate and the Ghurid dynasty and documented the details as they happened.
There are many more historical evidences that also prove Khilji’s destruction of Nalanda. Bakhtiyar Khilji not only destroyed Nalanda Univ but also executed the thousands of teachers/students and set fire to the 3 multi-storey libraries housing lakhs of manuscripts. This article by The Caravan started doing the rounds under the hashtag BuddhismVsBrahmanism. That’s how likes of Jha try to distort facts pointing Hindus as perpetrators at the same time igniting differences within Indian cultural identities with fake narratives.

On the left is a screenshot of the tweet by ‘The Caravan’ and on the left is an extract attached from Minhaj-i-Siraj’s book Tabaqat-i Nasiri translated by Raverty that describes how Khilji attacked, destroyed Nalanda University, killed the inhabitants (teachers and students).
What were the temple remnants discovered in the Ram jamabhoomi site before the Ayodhya verdict? Archaeologist KK Mohammed (honored with Padmashri award), the Regional Director (North) of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) earlier and currently the Project Archaeological Director for Aga Khan Trust for Culture revealed startling facts about the archaeological findings at the Ram Janambhoomi site in Ayodhya. It was before the Ayodhya verdict. His findings also strengthened the Ayodhya case. KK Mohammed extensively surveyed Ayodhya in 1978 as an archaeology student as a member of a team headed by Prof BB Lal. There were twelve students of School of Archeology Delhi and officials of the ASI. The surveying team spent around two months in various explorations in Ayodhya.
To quote an article published in Organiser, “The spirit of Ramajanmabhoomi movement is based on the crucial premise that the disputed structure was created after dismantling the Temple. Even before the movement the archaeological exercise was undertaken. The archaeological evidence collected by Prof Lal and his team, of which Dr KK Mohammed was a part, confirmed the presence of a huge pre-existing temple beneath the disputed structure. In his book, Njan Enna Bharatiyan, originally written in Malayalam, Dr Mohammad elaborated the whole process in this scientific exercise of revisiting history.”
The Babri Masjid, named after Babur, was built by Mughal Commander Mir Baqi following the orders of Babur in 1528–29 on a hill called Ramkot (Rama’s Fort). The site originally hosted a temple (it is still disputed whether the temple was of Shri Ram). Alf Hiltebeitel’s book Rethinking India’s Oral and Classical Epics: Draupadi among Rajputs, Muslims, and Dalits finds mention of Ramkot as Rama’s Fort – the central site of Ram Janambhoomi, the sacred land of Rama’s birth and about this place being discovered by Raja Vikramaditya. His research further quotes Peter van der Veer’s book in justification.

Archaeological Findings by KK Mohammed at Ram Janambhoomi site
1. There were brick foundations that supported the pillars of a pre-existed temple.
2. Temple-pillars, made of black stone Black basalt), were embedded on the walls of Babri Masjid.
3. Poorna Kalashas are found engraved at the bottom of the pillars. A poorna kalasha is a pot topped with a coronet of mango leaves and a coconut. The Vedas find mention of poorna kalasha as a symbol of abundance and ‘source of life’. It is part of daily worship in many a temple/home. No ceremonies like Griha Pravesh, etc. is complete without the poorna kalasha. Most existing temple pillars and walls have the poorna kalasha motif engraved in them. What does this motif in the pillars under Babri Masjid prove?
4. There were fourteen such temple pillars before the mosque was demolished in 1992.
5. Brick platforms on which the black stone pillars used to rest, were found during excavations at the back and sides of the mosque.
Based on the above findings, KK Mohammed ‘made a statement in 1990 that there existed a temple beneath the Babri Masjid’. To further quote KK Mohammed, “But a few Leftist historians allied themselves with the confrontationist Muslims and distorted the matter.”
Other Archaeological Findings at Ram Janambhoomi site
1. 263 temple related artefacts were found during leveling of the front yard of the Babri Masjid as per report submitted by Dr Ragesh Tiwari, Uttar Pradesh Archeology Director.
2. Stone plaque called Vishnu Hari Shila was found at site during demolition. Inscription in Nagari script in Sanskrit in this stone plaque mentions about the temple being dedicated to Vishnu (A single temple complex in ancient and medieval India hosted several temple dedicated to different deities.)
3. Small clay statues of Vishnu’s Avataras including statues of Shiva, Parvati, and other deities from the Kushana period dating back to 1st century CE were found during excavations in 1992.
4. Over fifty brick foundations that once supported the temple pillars were found during excavations in 2003.
Following the directions of the Allahabad High Court, the ASI conducted an in-depth excavation of Ram Janambhoomi site from 12 March 2003 to 7 August 2003. The survey during excavations resulted in 1360 discoveries. Based on its findings, the ASI submitted a report to the court. As per the summary of the report, remains of a 10th-century temple were found under the mosque.
Here is a video of a talk by historian and political scientist Meenakshi Jain on Ram Janambhoomi organized by Srijan Foundation.
It is no surprise that Islamic invaders destroyed thousands of temples and build mosques in many of those temple sites using materials of the broken structures. While there are hundreds of external evidences visible, in hundreds of cases, the evidences can be found buried underneath. Ayodhya is no exception!
Ref
1. Anthropology of Ancient Hindu Kingdoms: A Study in Civilizational Perspective, Makhan Jha
2. ‘Ayodhya: Truth I Knew, Truth I Said‘, K K Mohammed
3. https://www.rediff.com/news/2003/aug/22ayo.htm
4. https://www.tribuneindia.com/2003/20030826/main6.htm
5. American science channel says Ram Setu man-made, Deccan Chronicle.
The author of this piece Manoshi Sinha is an independent researcher of Indian History and ancient/medieval era temples.
Latest posts by manoshi sinha (see all)
- What if Shaikh Paltu had Helped Mangal Panday instead of British? - April 18, 2024
- Shivaleela: Celebration of Shiva in this 21st Century Gurukul - April 18, 2024
- INA Veteran Lt Madhvan Appeals for Installation of Statue of Rash Behari Bose in Delhi - April 18, 2024






